Objectives
Introduce the basic concepts of fluid mechanics including fluid properties, hydrostatics and fluids in motion.
Cover the applications of these concepts to allow students to calculate pressure distributions in static fluids, forces on immersed surfaces and pressure losses for steady incompressible flows in piping systems. The course also introduces the instrumentation used to measure pressure, flow velocity and flow rates.
In order to impart problem-solving skills, a large number of applied problems is treated in class and as homework.
————————————————————————-
Content
Introduction
· Definitions: Fluid, fluid mechanics
· Fluid properties: Density, Specific volume, Specific weight, Pressure, Temperature & Viscosity.
· Dimensions and units
Fluid Statics
· General equation of the pressure variation in a static fluid
· Pressure measurements: liquid manometers (simple, U-tube, inclined), barometer, Bourdon manometer, Piezoelectric pressure sensors, Strain gauge Transducer.
· Hydrostatic Forces on immersed surfaces: plane and curved
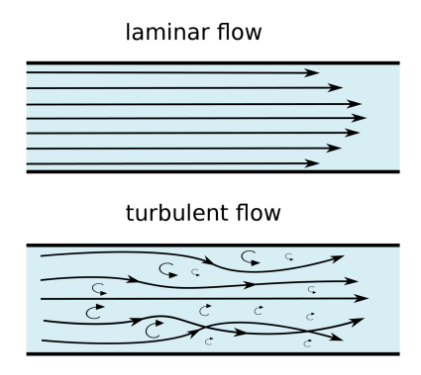
Fluid Flow
· Introduction, flow categories
· Equations of motion
· Flow meters: Venturi, orifice, positive displacement, turbine, vortex, ultrasonic, paddlewheel …
· Flow velocity measurement: Pitot tube, anemometers
· Applications of Bernouilli’s equation
· Modified Bernouilli’s equation
· Head losses: major and minor losses
. Analysis of piping systems

